Oracle Risk and Security Standards: An Introduction (Pt. 1)
Introduction
At Chaos Labs, our focus is deeply rooted in blockchain protocol risk and security – an area we view as intrinsic to the growth and adoption of DeFi. Oracles are at the heart of DeFi (whether you like it or not) and have powered crypto applications since 2017, securing over $50 billion today.
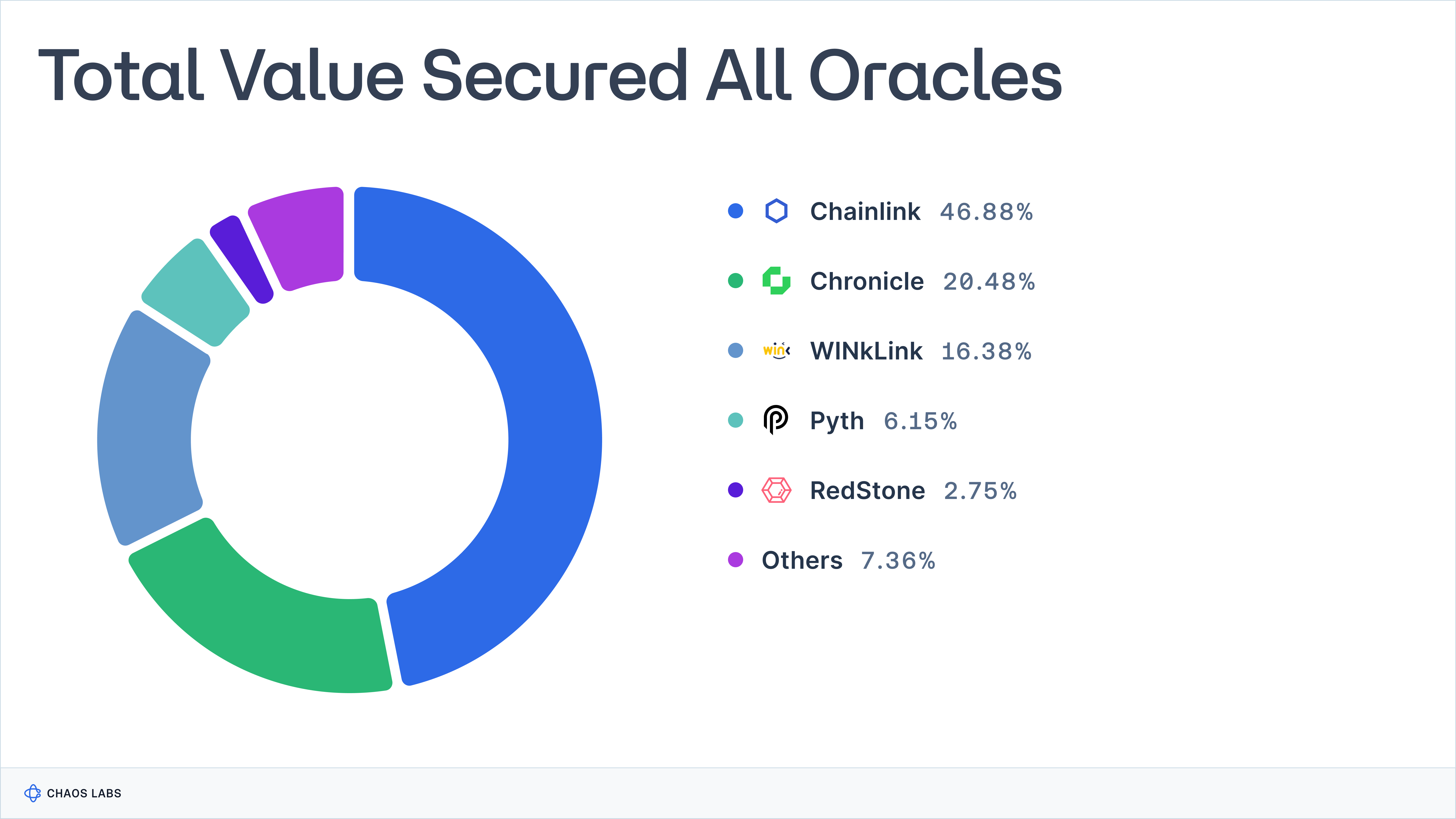
The role of Oracles cannot be overstated; Oracles facilitate nearly every transaction within the blockchain sphere, becoming an essential cog in the DeFi machinery.
DeFi applications revolve around the creation and maintenance of trustless systems. This vision challenges the conventional reliance on trust, advocating for a transparent and autonomous infrastructure. Yet, in a somewhat paradoxical twist, oracles – the elements tasked with feeding critical, real-world data into blockchains – are held in high regard and trusted implicitly by developers and users alike. This trust stems mainly from a lack of understanding about how oracles function and the risks they carry.
At Chaos Labs, we aim to pivot from this dependency on trust towards a comprehensive understanding of oracles. Our objective is twofold: to demystify oracles' operational intricacies and highlight the potential risks they introduce to DeFi projects. We believe trust can be significantly reduced by creating an environment where developers and users are well-informed about the mechanisms powering their applications.
Understanding oracles, the data they provide, and the implications of their use is not just about enhancing security—it's about empowering the entire DeFi ecosystem to make informed decisions, reinforcing the foundational principles of decentralized finance.
To improve industry-wide risk and security posture and reduce protocol attacks and failures, we’re open-sourcing our Oracle Security and Architecture Standards Framework. Our Oracle Security Framework is the inspiration for our Oracle Security and Risk Platform. It has been developed as part of our work in leading, assessing, and auditing Oracles for top DeFi protocols.
We hope this can serve as a canonical reference for application builders and mechanism designers to utilize when selecting Oracle solutions for their applications, to better understand the pros and cons of each Oracle, and to properly understand architecture advantages and risk surfaces. With this, let’s dive in. Part one of this series will frame Oracle's utility and impact and lay a foundation for the pillars we will explore in this multi-part series.
Why Should I Care About Oracles?
Oracles aren't just infrastructure for DeFi applications; they are often the lifeblood that powers them. To better understand the value of Oracles, let’s first align on why Blockchains, without Oracles, are limited in terms of applications they can support.
Blockchains are Closed Networks and Deterministic State Machines
Out of the box, a Blockchain can perform three functions well.
- Immutable and Auditable Transaction History: The core of blockchain technology is its distributed ledger, which records all transactions across a network of computers. This ledger provides a permanent and immutable record of asset ownership and transaction history. Its decentralized nature ensures that it is resistant to tampering and fraud, making it a reliable source for tracking asset ownership and state.
- Authorization Service via Cryptographic Signature Verification: Blockchains utilizes advanced cryptography, mainly through private/public key pairs. This aspect enables the blockchain to verify the authenticity of transactions securely. Each user on the blockchain has a unique pair of keys; the public key is visible to everyone and is used to identify the user, while the private key is kept secret and is used to sign transactions. This cryptographic method ensures that transactions are secure and can be attributed to a specific user, enhancing trust and security in the network.
- State Machine with Turing Complete Programming Languages: Modern blockchains, especially those like Ethereum, offer Turing complete programming languages. This feature allows the creation and execution of smart contracts—self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code. These contracts can initiate state transitions on the blockchain, which are then recorded and tracked. This programmability and expressiveness allow for a wide range of applications, from decentralized finance (DeFi) to non-fungible tokens (NFTs) and more complex decentralized applications (dApps). The ability to record the history of these state transitions on-chain provides transparency and a tamper-proof record of all interactions and transactions.
Isolated blockchain networks necessitate Oracles to access real-world data and function effectively.
Connecting the External World to Blockchain Networks
Oracles serve as data bridges between the blockchain and the external world. They provide a way for blockchains to interact securely and reliably with external information. This interaction is vital for many blockchain applications, particularly those that rely on real-world data, such as prices, weather information, or any other external data.
Catalyst for State Transitions
If we view the blockchain as a state machine, oracles trigger state transitions based on external data. For instance, a smart contract on a blockchain might be designed to execute a particular action, like a liquidation, when the price of gold reaches a certain level. The oracle is responsible for providing the blockchain with the current price of gold, enabling the smart contract to execute its code based on this external data.
The Oracle Problem
The "Oracle Problem" stems from the blockchain's inherent limitations as a closed-loop system, where applications can only access and react to data within the blockchain itself. While securing the blockchain, this isolation restricts its ability to directly utilize real-world data, which is crucial for many decentralized applications that require external information to operate effectively.
Oracles address this limitation by acting as intermediaries, securely integrating external data into the blockchain. This process updates the blockchain's state with vital information from the outside world, enabling dApps to execute transactions based on accurate and current real-world data.
In essence, oracles bridge the gap between the blockchain's secure, isolated environment and the dynamic, information-rich external world, making them indispensable for the functionality and utility of dApps that depend on real-world data to make informed decisions.
Why Can’t My Application Connect Directly to an API?
The blockchain's distributed ledger nature mandates that each node in the network reaches a deterministic output given identical input, enabling consensus among nodes during transaction validation. For example, in a transaction where $10 is transferred from Bob to Alice, each node independently adjusts Alice's balance by adding $10 and deducting the same amount from Bob's account, ensuring uniformity across the network.
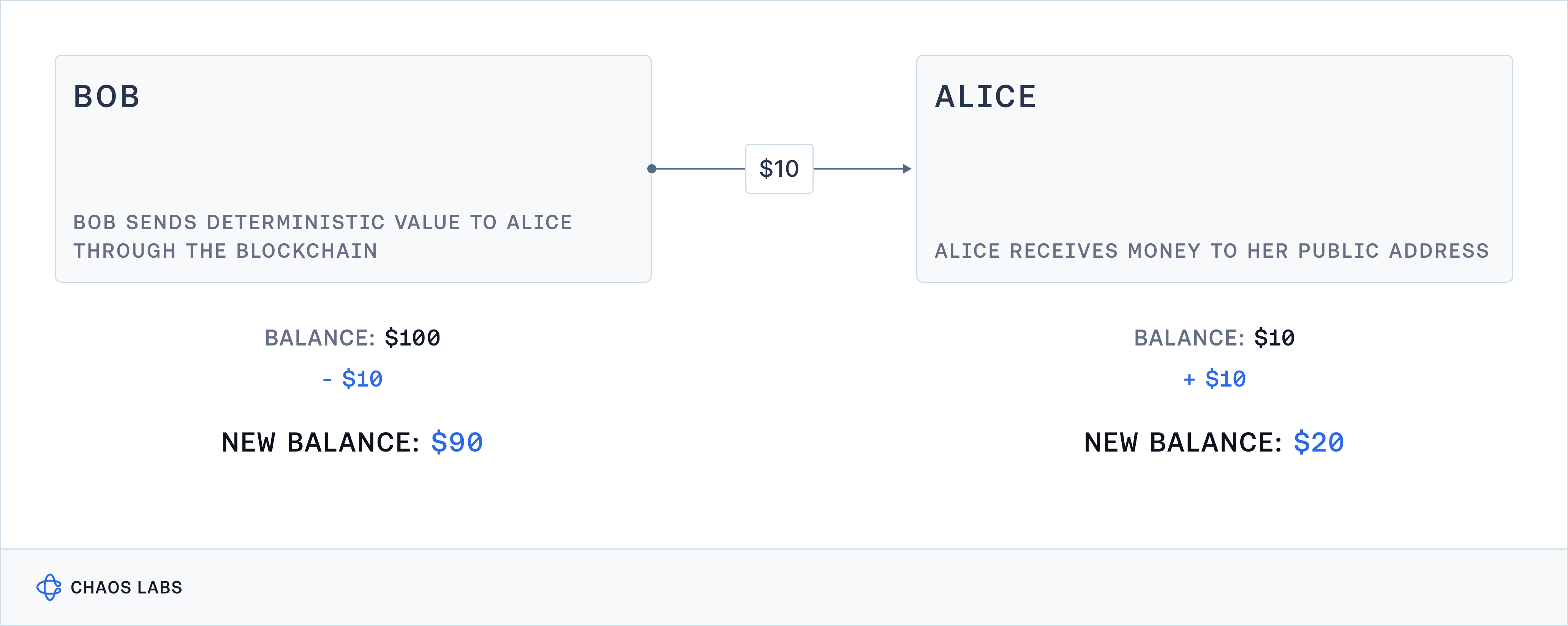
However, determinism faces challenges when external APIs are employed to validate transactions. Consider a scenario where Bob’s transfer to Alice’s contract relies on an API to determine the amount to transfer based on the price of ETH.
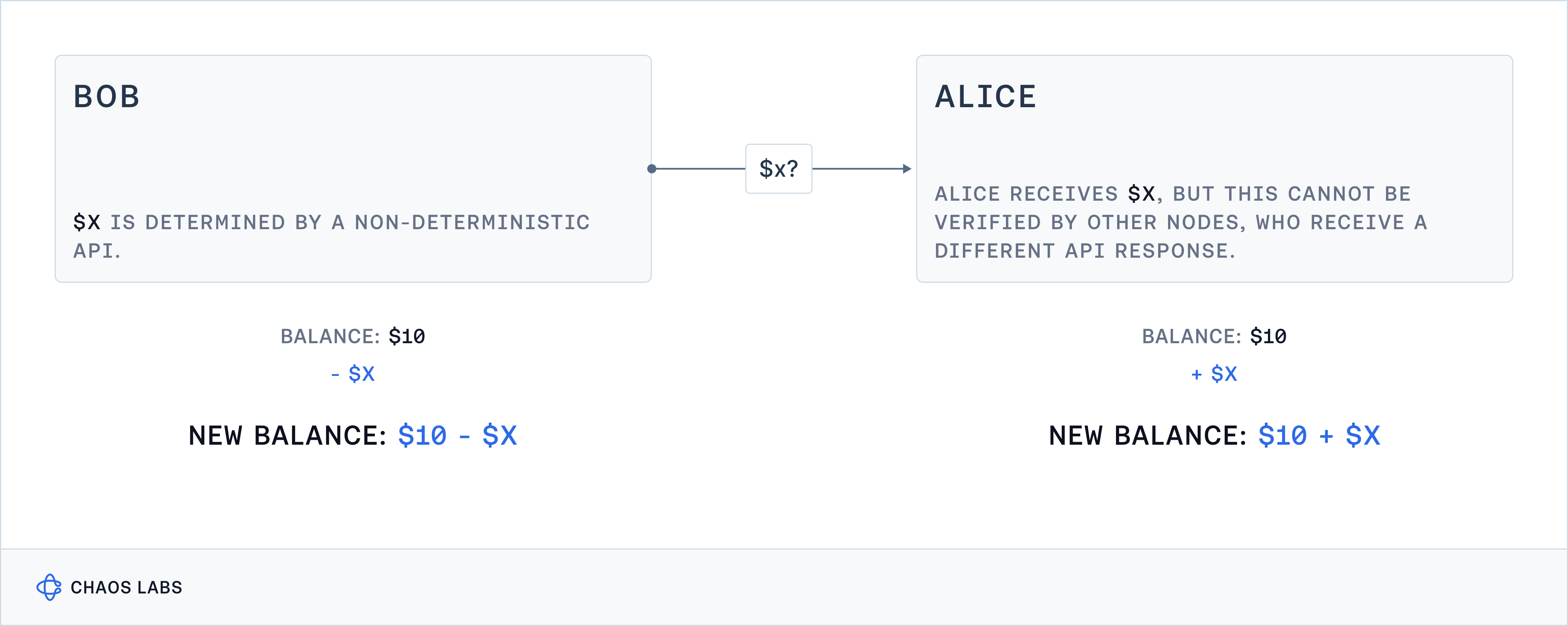
Several factors contribute to inconsistent data inputs:
- Nodes may access the API at varying times, resulting in discrepancies due to changes in API data, even with microsecond differences in API calls.
- Nodes may encounter rate-limiting issues and receive no response or stale responses from the API.
- Geographical distribution can route nodes to different API services, yielding different responses.
These challenges highlight the non-deterministic nature of API-driven data responses, which can lead to a lack of consensus among nodes regarding the blockchain's state, whether due to malicious intent or, discrepancies in latency or rate limiting.
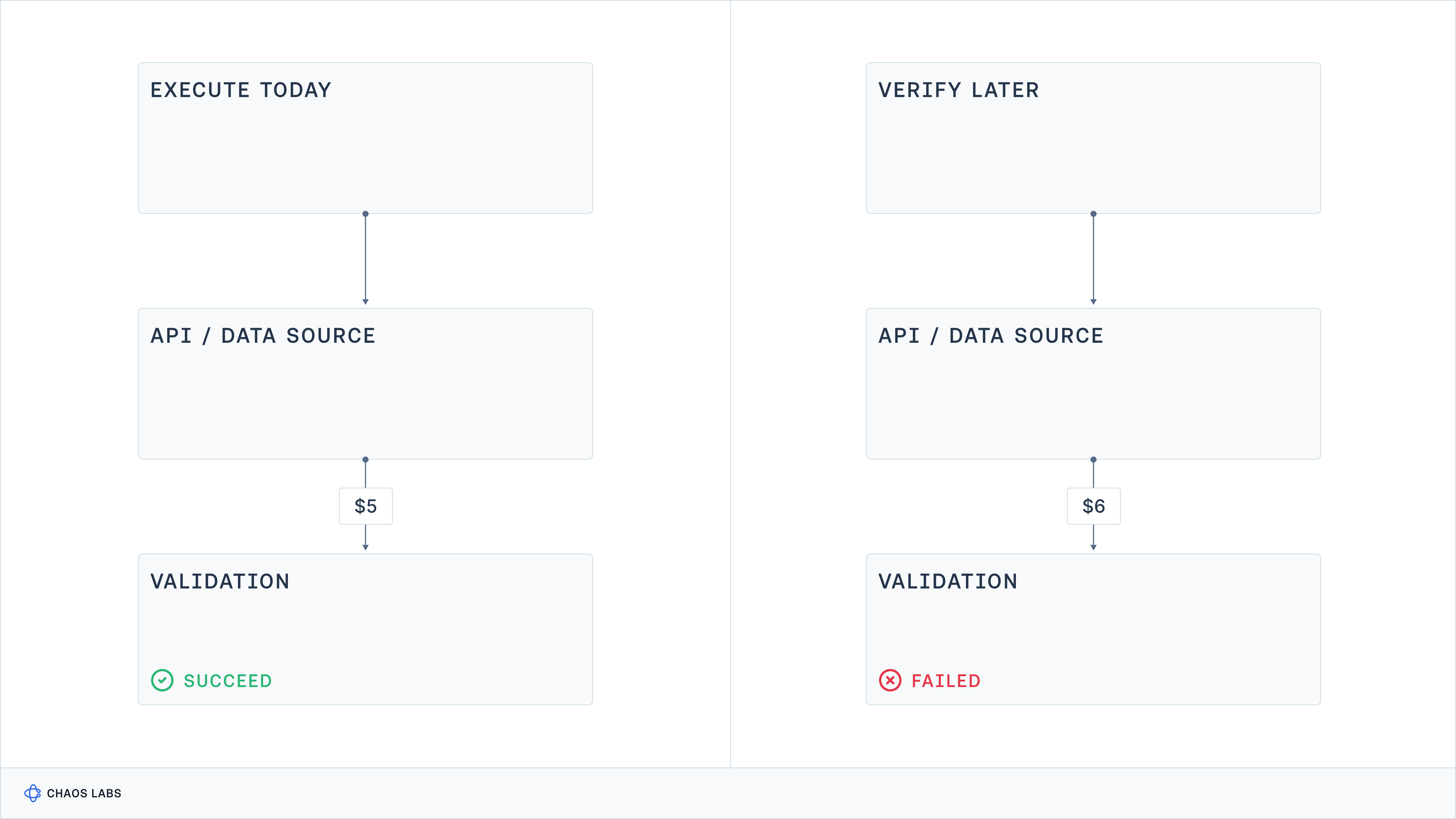
To preserve consensus, blockchain networks prioritize determinism, ensuring that replaying transactions always yields the correct state. However, integrating real-world data into blockchain poses a challenge due to the deterministic constraint, which is critical for applications like DeFi and decentralized insurance.
Blockchain oracles are intermediaries, bridging the gap between deterministic blockchains and off-chain data sources. By inputting external data into the blockchain through transactions, oracles maintain their self-contained nature and enable them to verify their state. This middleware role underscores the significance of oracles in connecting the blockchain world with external data sources.
Despite their crucial role, oracles encounter challenges, commonly called the "oracle problem."
The Oracle Landscape
Oracles are complex entities with extensive risk and security surface areas, necessitating a deep dive into their operations and advancements. The evolving landscape of oracles, marked by recent technological advances and performance enhancements, presents a promising future. This series explores the next frontier in oracle technology: low-latency, high-throughput oracles. Such oracles are the backbone of transaction settlement, providing mission-critical data while targeting efficiency. While numerous oracle types exist, we will focus on a select few, offering insights into their functionality and potential impact on the decentralized finance (DeFi) space. For a complete picture, we list prevalent Oracle types below.
On-Chain Oracles
On-chain oracles come in many flavors. The most prevalent Onchain Oracles are Time-Weighted Average Price (TWAP) oracles, which calculate current prices through historical observations. A notable example is the Uniswap V3 TWAP oracles, which derive asset prices from concentrated liquidity Automated Market Maker (AMM) pools. These oracles prioritize robustness against market manipulation by relying on historical data, albeit at the cost of precision. Their application becomes particularly relevant (potentially risky) in inadequate Centralized Exchange (CEX) liquidity scenarios.

Chaos Labs has previously researched the Risks of Uniswap V3 TWAP Oracles.
Push-Based Oracles
Initiated by Chronicle and popularized by Chainlink, off-chain, push-based oracles represent the dominant Oracle in DeFi today. These oracles deliver fresh data based on predetermined, discrete parameters: a time-based trigger (aka “the heartbeat”) and a volatility/price action trigger. Chainlink’s push-based oracles inherit a volume-weighted average price (VWAP) methodology from data sources that also employ outlier detection mechanisms.
Today, these oracles are the pre-eminent model in DeFi, securing most borrow/lend applications, among other use cases.
Pull-Based Oracles
This series focuses on exploring the forefront of oracle innovation: pull-based oracles. Spearheaded by pioneers like Chainlink and Pyth and offered by additional protocols such as Redstone and Stork, pull-based oracles represent a significant leap forward in oracle technology. Their development is driven by the demand for cost-efficient, high-precision, low-latency data critical for high-throughput derivative trading platforms, such as those handling perpetual exchanges.
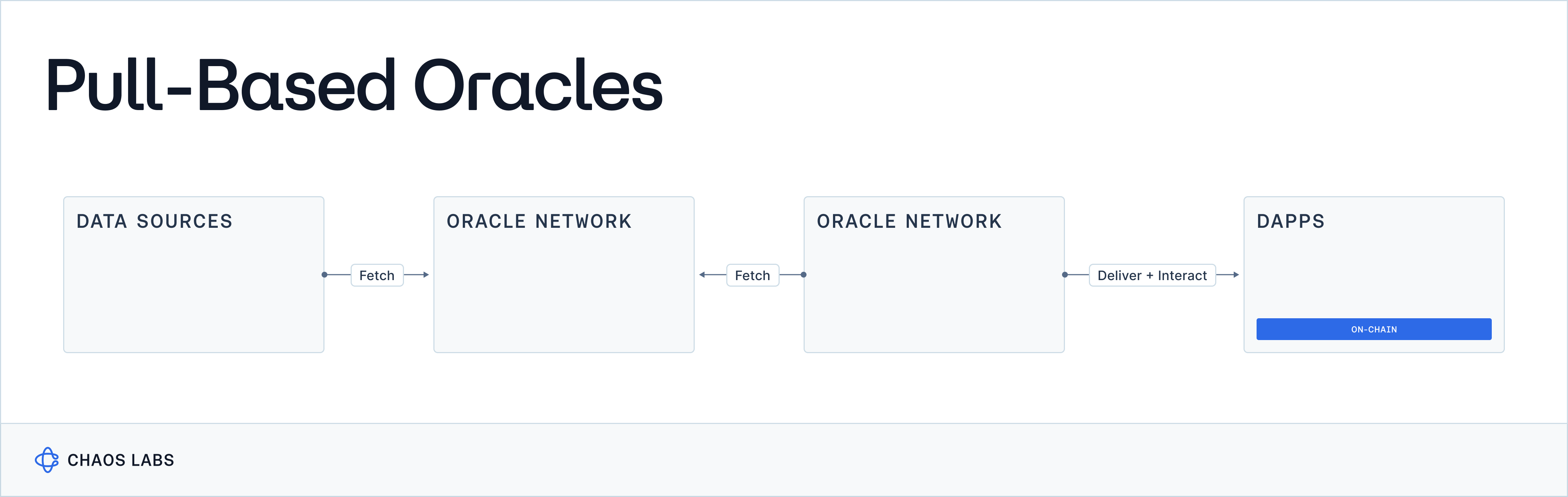
The advent of pull-based oracles marks a paradigm shift in how trading data is utilized across blockchain networks, offering a speed and accuracy previously unattainable. These oracles are at the forefront of addressing a critical need within blockchains aimed at serving as the global financial settlement layer. The essence of finance—a domain where propagation latency and precision are indispensable—demands these characteristics without compromise. Any delay in data delivery or lack of precision introduces information asymmetry, laying the groundwork for economic exploits and an inequitable financial system.
As we delve deeper into the capabilities and applications of pull-based oracles, we aim to illuminate their critical roles, unpack the complexities they navigate, and outline the evolving dynamics of oracle technology within blockchain ecosystems. This exploration will highlight the cutting-edge developments in Oracle technology and underscore the importance of these innovations in supporting the next generation of blockchain applications.
Chaos Labs has previously conducted an audit of Chainlink Low-Latency Oracles on behalf of GMX, and monitors data feeds in real-time to ensure precision and uptime.
Learn more about Chaos Labs Oracle audits here.
The Scale of the Oracle Security Problem
To better understand the scale of this challenge, let’s look at 2022: the crypto world witnessed a staggering loss of over $3.8 billion to hacks, with DeFi protocols and bridges being the prime targets. These breaches weren't all due to flagrant security lapses. In many cases, even protocols developed by the most reputed teams that followed the so-called gold standards of security practices found themselves exploited. This tells us something profound: the challenge isn't merely about ramping up our security efforts. It's about reimagining and reengineering our strategies to stay ahead of an ever-evolving threat landscape.
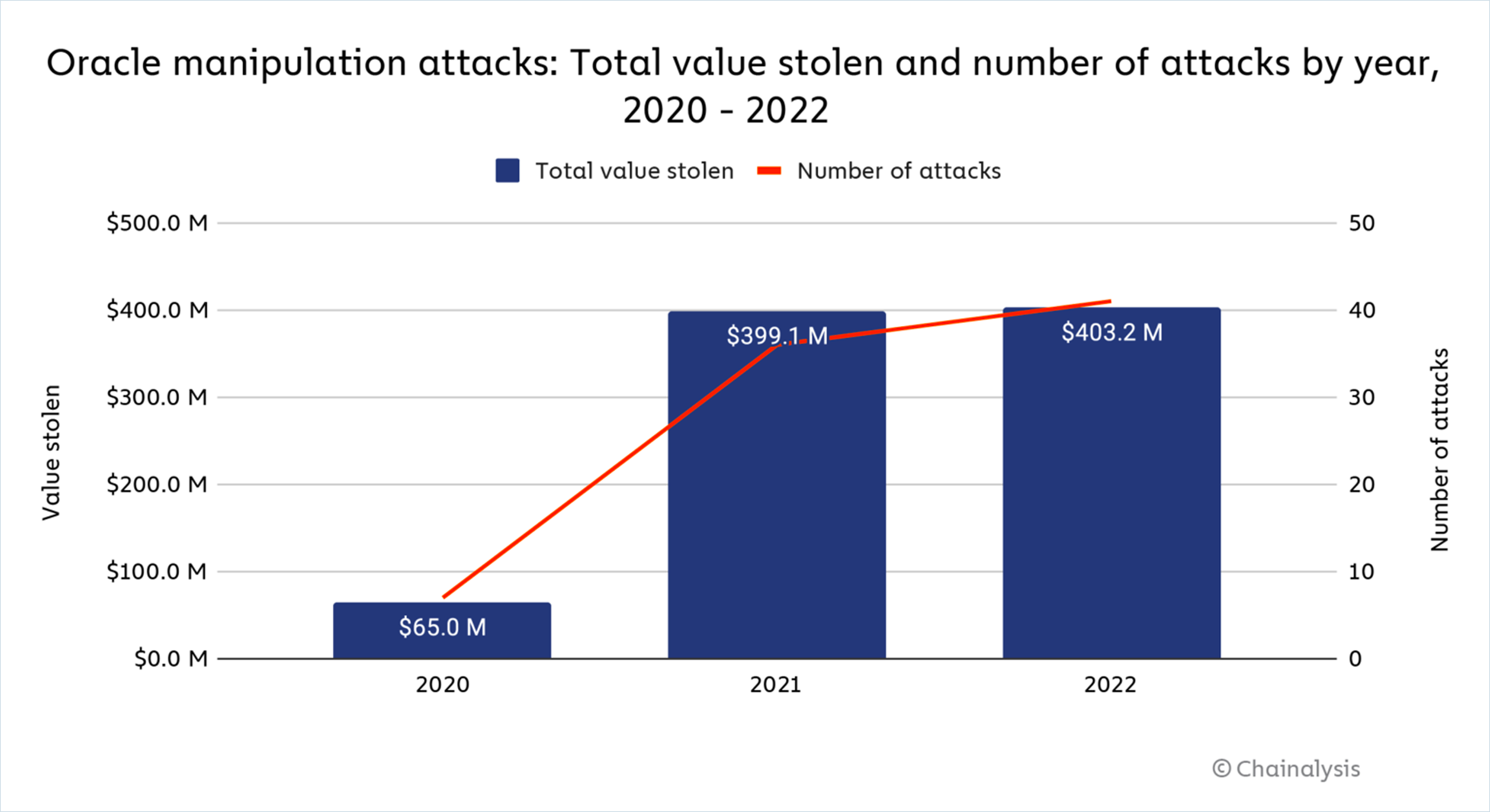
So, to our point, why should you care about Oracles? Off-chain data and oracles are mandatory for building financial applications with real-world use cases; we now understand we have a severe problem. Oracle security must be improved 10x for our industry to see meaningful adoption. After all, why would anyone migrate to a riskier, less secure financial system? From a developer perspective, getting Oracle security right from the get-go is critical. When exploited, Oracle failures and manipulations are fatal - very few protocols recover from these. Also, as a protocol founder, this security question isn’t something you get to delegate or outsource. Your users don’t care if the exploit was rooted in a third-party vendor. The bottom line is they were exploited on your platform—as a builder, you’re responsible for diligencing the vendor, the technology, and the quality of the solution. If you’re a serious founder, the Pandora’s Box of Third Party Mission-Critical Data should keep you up at night.
Is Mission-Critical Third-Party Data Security a Novel Web3 Challenge?
A direct analogy in the Web2 domain is the security of third-party APIs in mission-critical applications. This involves ensuring the secure integration and use of external APIs—crafted and controlled outside your organization—within your software infrastructure. Given the reliance of crucial software on data or functionalities from these third-party APIs, securing these connections is paramount to preventing data breaches, upholding data integrity, and ensuring software reliability. Web2 addresses these challenges through high-trust, centralized strategies, including contractual agreements on data quality (Service Level Agreements, or SLAs), compliance with standards, and legal frameworks. However, the Web3 ecosystem, built on the ethos of decentralization, demands trustless mechanisms. This paradigm shift introduces a more complex layer to securing third-party data integrations. In a trustless environment, where traditional off-chain resolutions like legal recourse or SLAs with a counterparty aren't viable, the onus falls on devising more innovative, inherently secure data integration and security models. The move towards trustless systems necessitates reimagining how we approach and solve third-party data security in the decentralized world.
What is the Oracle Security and Architecture Standards Framework?
Oracles are core to blockchain-based financial applications, vastly expanding the world of what is possible with otherwise closed network blockchains. As risk providers and managers for the largest DeFi protocols in the industry, like Aave, GMX, and more, we work closely with core contributors, developers, and founders to map and address application risk vectors. If we think of blockchains and protocols as state machines, Oracles, as we will see below, are the main catalysts for application state transitions. Unfortunately, the name Oracle can be a misnomer, as by definition, we are led to believe Oracle data can always be trusted:
In English, the term "oracle" historically refers to a person or a medium believed to provide wise and insightful counsel or prophetic predictions or precognition of the future, inspired by the deities. This concept originates from ancient cultures and religions where oracles played a significant role in decision-making processes, offering guidance through divine communication. The most famous example is the Oracle of Delphi in ancient Greece, where individuals or state representatives would visit to seek advice or predictions about their futures, wars, or the will of the gods.

However, Oracle failures and manipulations (for the “it’s not Oracle Manipulation, it’s Market manipulation” crowd we’ll dive into during this series) are rampant. The security and reliability of Oracle data are directly tied to the weakest link in the Oracle data supply chain.
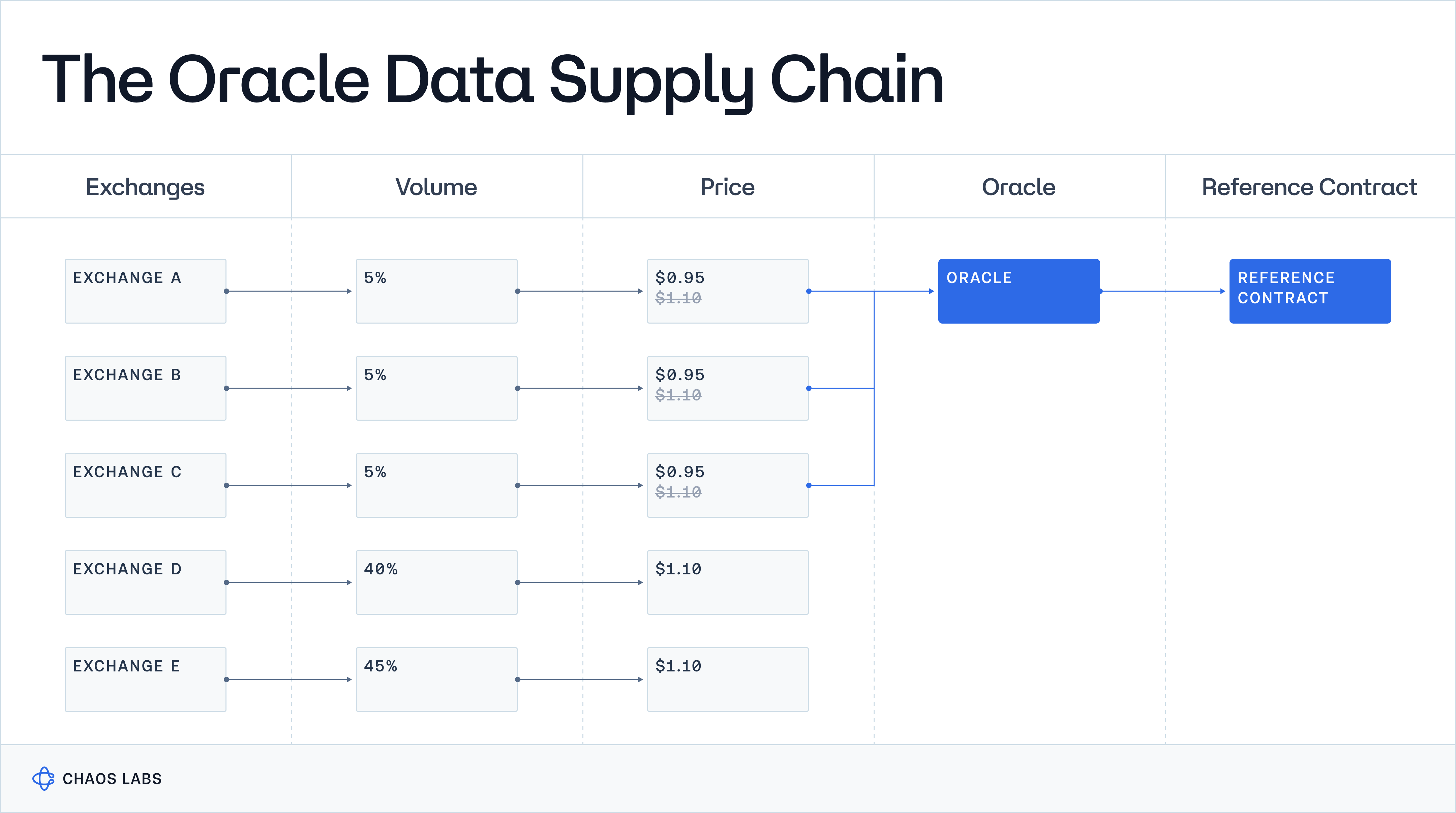
Similarly critical is how applications sanitize and consume this data. In our opinion, mission-critical software applications (DeFi protocols managing billions of dollars) blindly consuming Oracle data with no risk engine, i.e., business logic checking whether or not the data makes sense or triggers sensible state transitions, is crazy.
Our discussion on Standards and Frameworks begins by outlining the basic building blocks of Oracles, establishing a solid foundational understanding, and, subsequently, examining the different risk surfaces and attack vectors.
Oracle Standards Framework
The Oracle Standards Framework begins with examining Oracle architectures and topologies, laying the foundational groundwork for our exploration.
This initial review is critical for segmenting the security and risk framework into distinct pillars. These pillars, when combined, form the essence of an Oracle. In the ensuing series, we will delve into each of these high-level pillars, providing a thorough analysis and insight into the pivotal components in the construction and operation of Oracles.
Oracle Standards Framework: Scoring Oracle Security and Risk
The objective is to develop a standardized methodology for comprehensive DeFi Oracle Ratings. This will ensure the security and reliability of on-chain data feeds and streams, making them suitable for consumption by DeFi protocols, mainly focusing on derivative instruments sensitive to precise and manipulation-resistant data streams.
Chapter 1: Oracle Network Architecture and Topologies
Chapter 1 delves into the Oracle Risk and Security Framework's first critical aspect: Oracle Network Architecture and Topologies. This post is designed to offer a comprehensive exploration across three verticals:
- Overview of Decentralized Oracle Network (DON) Architectures: This segment examines the various architectures that define decentralized Oracle networks. It highlights these architectures' distinct characteristics and operational methodologies, setting the stage for a deeper understanding of their roles within the Oracle ecosystem.
- Dissecting the Data Supply Chain: The narrative then examines the data supply chain within these networks. We will explore the processes involved in data sourcing, validation, and distribution, offering insights into the complexities and challenges of ensuring data accuracy and reliability in decentralized environments.
- Analyzing Network Topology and Data Flow Security and Risk Vectors: To conclude our exploration, we focus on the building blocks of Oracle networks. This part aims to unravel the network's composition, examining how individual components interconnect to form a cohesive and functional network structure crucial for Oracle's operational efficacy.
Chapter 2: Price Composition Methodology
This chapter will offer a structured preview of how oracles compose prices, the challenges and implications involved, and the methodologies that ensure accuracy and reliability.
Chapter Preview
- Introduction: We set the stage by outlining the chapter's aim to dissect the complex methodologies behind oracle price composition and their critical implications.
Core Sections
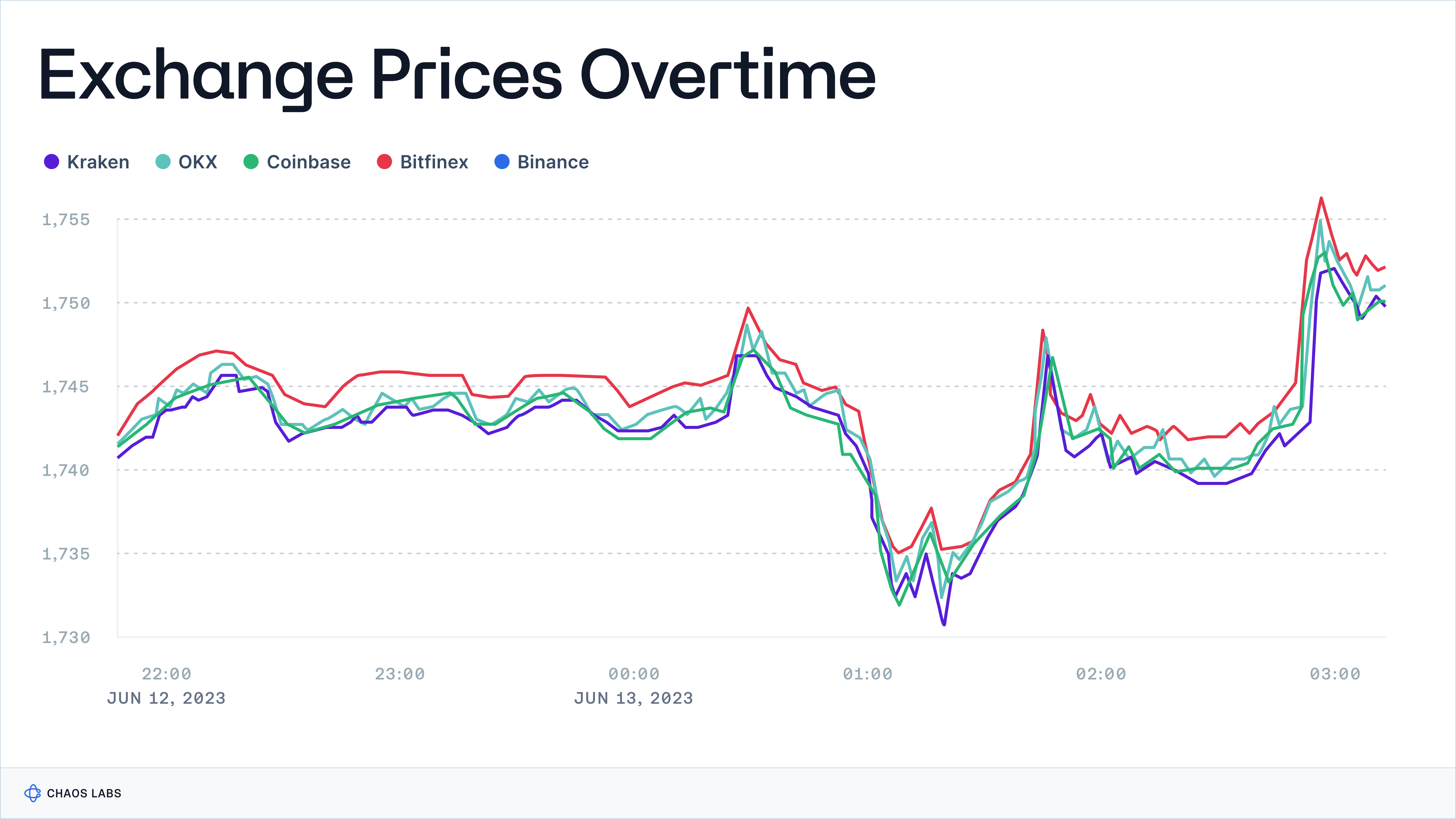
- Data Sourcing and Validation: The discussion will revolve around selecting exchanges and liquidity sources, defining the Relevant Market, and the necessity of ongoing market data monitoring.
- Pricing Methodologies: We critique commonly used methods like Last Trade Price and VWAP, propose alternative approaches for more accurate pricing, and explain the consolidation of order books for benchmark pricing.
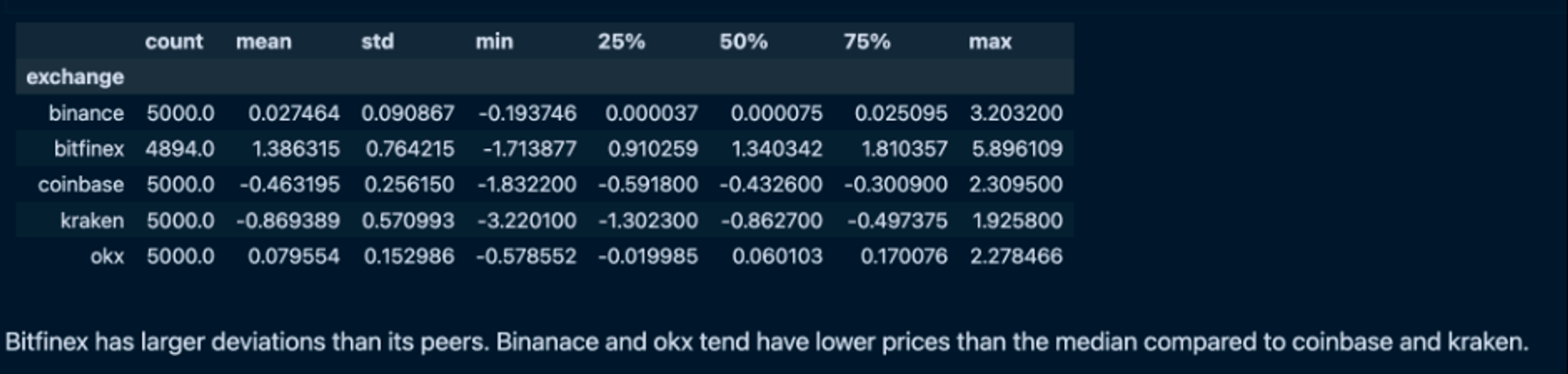
- Price Aggregation Techniques: An exploration of various aggregation methods, including Chainlink’s median approach and Pyth’s outlier removal technique, alongside a discussion on the trade-offs between different oracle models.
- Addressing Illiquid Assets: Strategies to enhance price quality for illiquid assets are examined, highlighting the challenges of simplistic pricing methods.
Means to Audit
- Emphasis will be placed on the transparency of price construction methods, the disclosure of approved exchanges for price sourcing, and methods for comparing price quality, supplemented by historical data analysis.
Case Studies and Examples
- Real-world incidents highlighting the importance of accurate price composition will be reviewed, and reasonable deviation metrics in pricing will be discussed.
Conclusion
- A summary of the methodologies discussed and their implications on Oracle accuracy and reliability will underscore the chapter's significance in the broader context of Oracle functionality.
Chapter 3: Oracle Data Replicability
This chapter ventures into the essential aspect of ensuring data replicability within Oracle systems. This chapter is meticulously designed to unpack the concept of data replicability, emphasizing the ability to trace and verify the inputs leading to the final price reported by oracles.
Chapter Preview
- Understanding Data Replicability: This paper introduces data replicability in the context of Oracle services, highlighting its significance for transparency and trust in decentralized finance (DeFi) systems.
- Tracing Inputs for Price Determination: Detailed exploration of methods and technologies that enable users and developers to trace the data inputs used in Oracle price reports. This section sheds light on how oracles aggregate and process data to arrive at a reported price, ensuring that users can independently verify and replicate these results.
- Challenges and Solutions in Data Replicability: Addressing the common challenges in achieving data replicability, including data source diversity and aggregation complexities. We will discuss innovative solutions and best practices that Oracle services can adopt to enhance the traceability and reliability of their data inputs.
- Implications for Oracle Reliability and User Trust: Concluding with a discussion on the broader impact of data replicability for Oracle reliability and the overall trust in Oracle services by the DeFi community. This section will emphasize why replicability is not just a technical requirement but a cornerstone for building user confidence in decentralized applications.
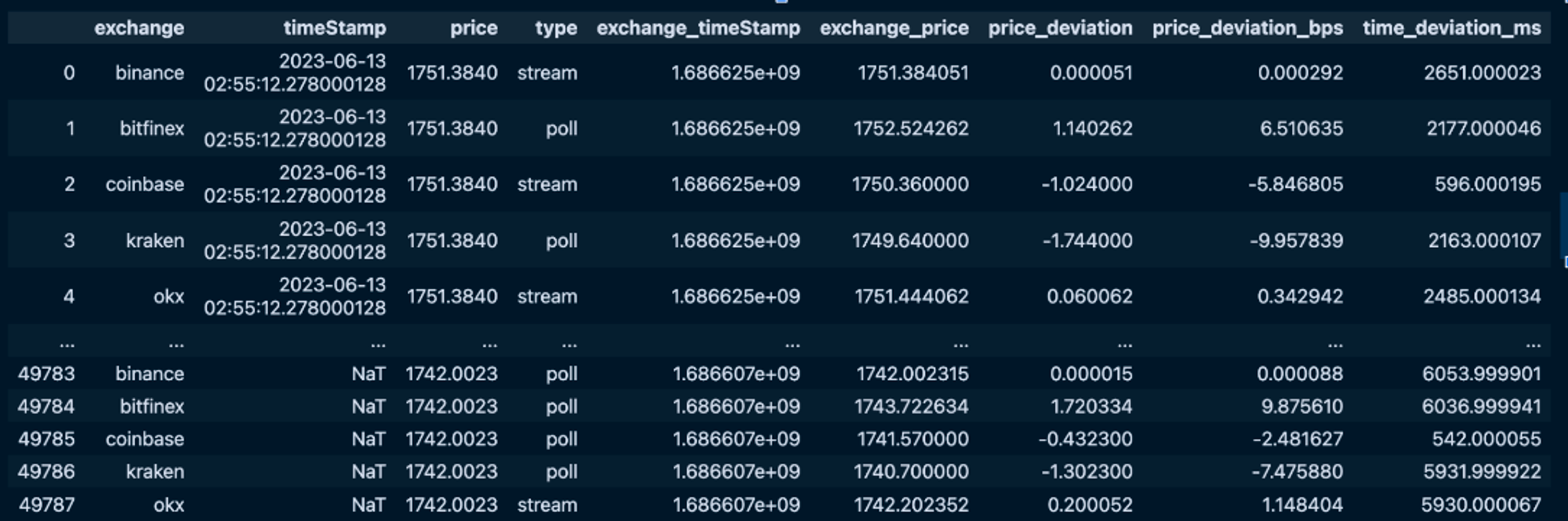
This chapter aims to provide a deep dive into the nuances of ensuring data replicability in Oracle services, offering readers insights into the technical and operational measures that can bolster transparency and trustworthiness in DeFi's critical infrastructure.
Chapter 4: Data Freshness, Precision and Latency
Chapter 3 underscores the critical importance of data freshness and precision in Oracle protocols, setting the stage with real-world examples (MNGO, GMX, FRAX, USDC depeg) that showcase the severe impacts of latency and imprecision.
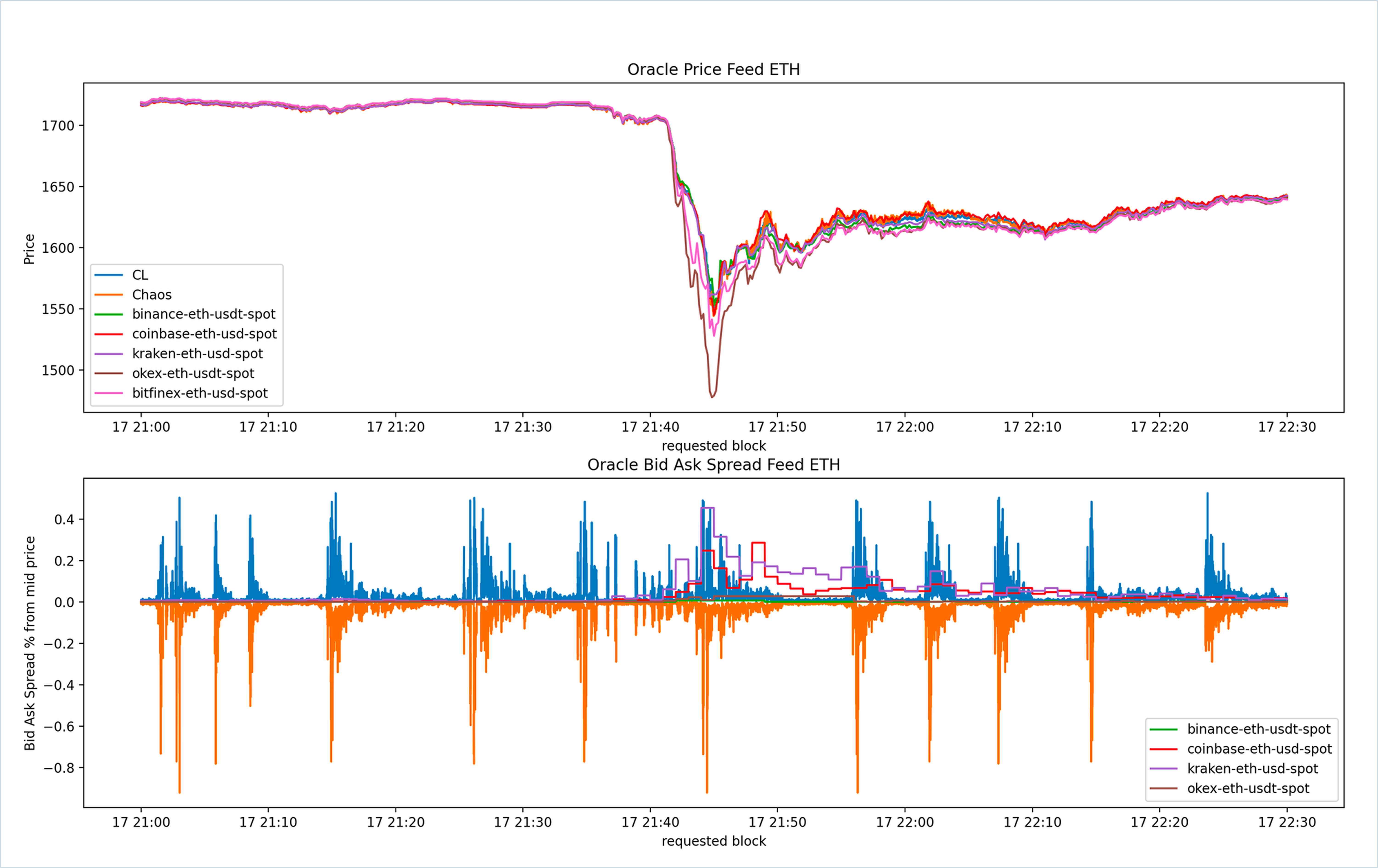
Understanding Latency and Freshness
- Definitions of critical terms pave the way for a deeper dive into data transport latency, identifying improvement areas to enhance data freshness.
Metrics and Measures for Oracle Data Streams
- Discussion on the necessity of stable update frequencies and low latency highlights the operational needs to mitigate front and back running, supported by objective data demonstrations.
Detailed Requirements
- We explore how the number of feeds and endpoint processing tasks influences system load, leading to a comprehensive explanation of latency calculation and its critical role in maintaining data freshness.
Chapter 3 presents an in-depth exploration of data latency and precision, combining theoretical understanding with practical examples to highlight the significance of Oracle security.
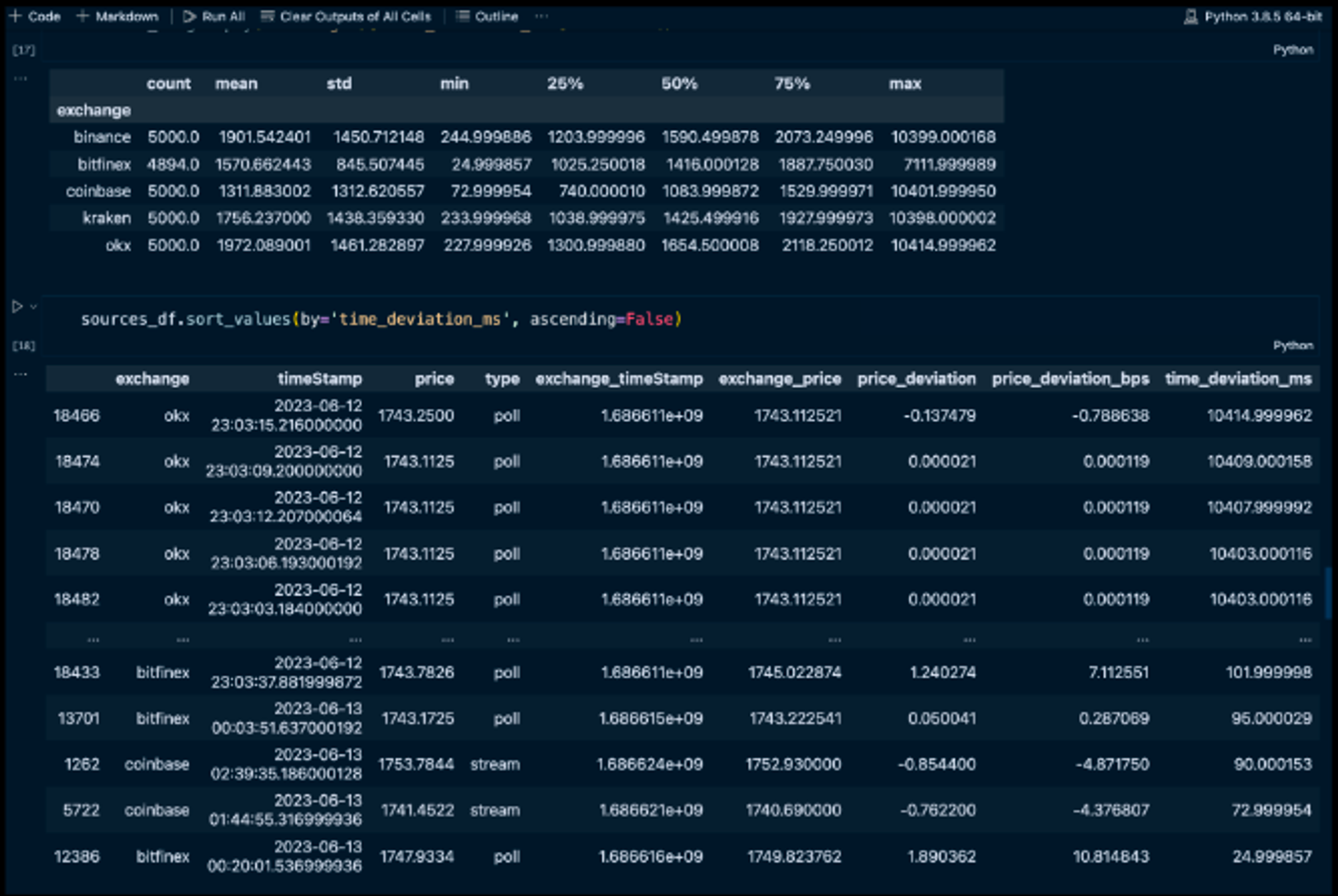
Chapter 5: Ensuring Reliability in On-chain Price Reporting
This chapter will navigate the methodologies and best practices designed to bolster the dependability of on-chain price data. This chapter is organized to provide a comprehensive understanding of achieving and maintaining high-reliability standards in reporting on-chain prices, alongside insights into managing report gas costs and evaluating performance.
- Reliable On-chain Reporting Framework:
- We begin with crafting a streamlined process and checklist to achieve consistent and reliable on-chain price reporting, emphasizing the integration of redundancy measures and fail-safe mechanisms to guarantee continuity.
- The chapter further delves into defining and managing operational risks, focusing on the challenges posed by off-chain data delivery mechanisms.
- Performance Monitoring and Evaluation:
- A dedicated section on establishing a robust framework for the ongoing monitoring and evaluation of performance, ensuring that on-chain price reporting remains accurate, timely, and cost-effective.
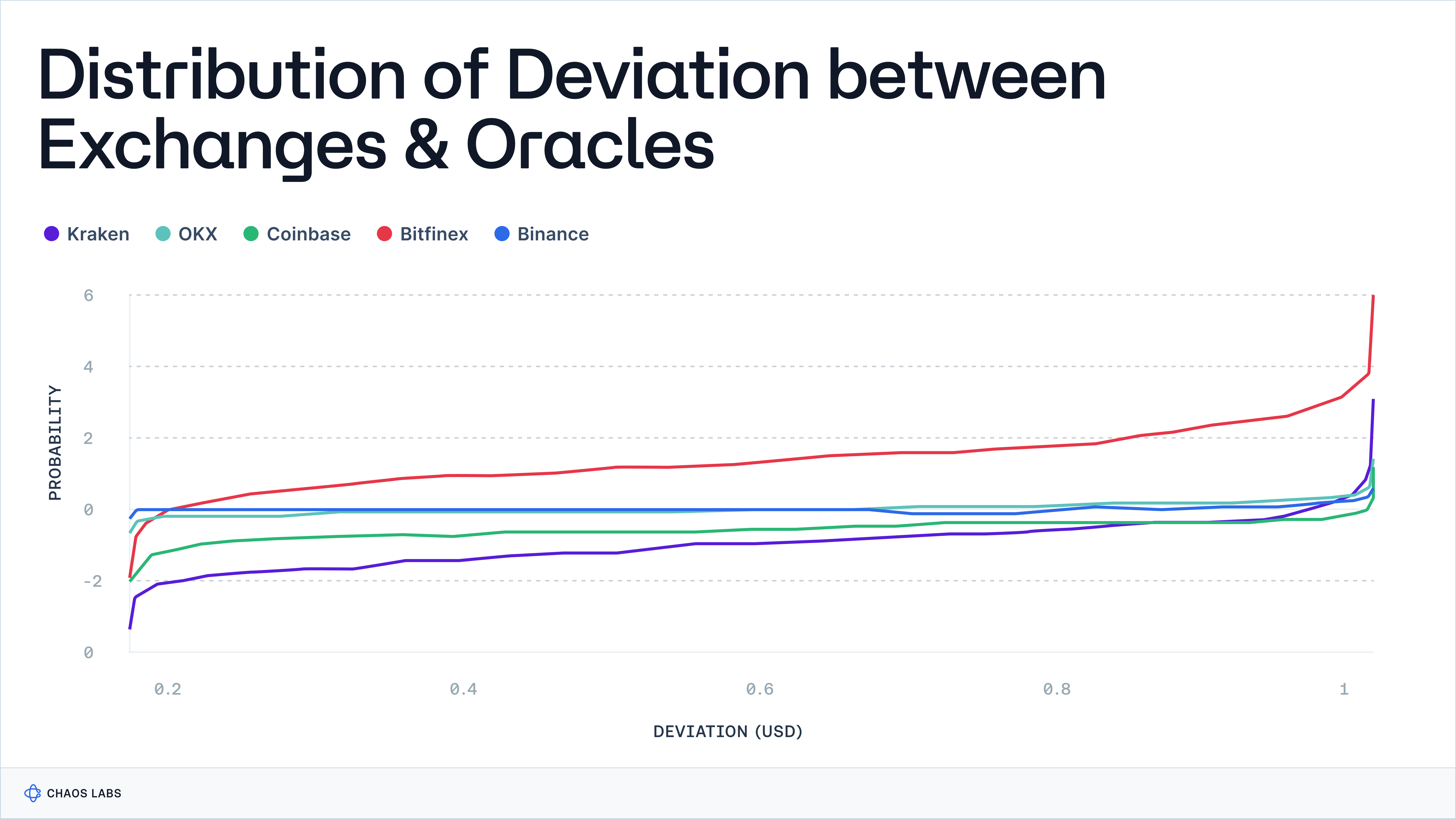
This chapter promises to equip readers with the necessary tools and knowledge to design, implement, and maintain reliable on-chain price reporting systems. By addressing key areas such as operational risk management, performance evaluation, and the intricacies of reporting gas costs, we aim to thoroughly explore the critical aspects of reliable on-chain data provision in the decentralized finance ecosystem.
Chapter 6: MEV and OEV Landscape
Mitigating MEV and OEV Risks
We begin by detailing the perils of pre-settlement data exposure, highlighting how advanced knowledge of Oracle updates can create arbitrage opportunities through frontrunning, supported by real-world incidents like hedera-hashgraph, Flashbots, and MEV-Boost-Relayer.
The discussion extends to potential solutions and their inherent trade-offs, emphasizing the primary goal of minimizing frontrunning while preserving fair user competition.
Analyzing Commit-and-Reveal Schemes
- This section delves into the mechanics of commit-and-reveal schemes employed by platforms such as Synthetix and GMX, with a case scenario involving Alice and Bob to illustrate operational dynamics and limitations.
- Despite these mechanisms, we explore how MEV activities and liquidations can still exploit these systems, proposing enhancements to mitigate such vulnerabilities.
Current Liquidation Practices and User Protection
- We examine the impact of current liquidation practices on users through the lens of Oracle accuracy and close factor setup, enriched by case studies from prominent Borrow/Lend DeFi protocols.
- From the liquidators' perspective, motivations and risks, including gas costs, market, duration risk, and capital efficiency, are discussed, leading to strategies to protect users and ensure a fair liquidation process.
This chapter aims to equip readers with a deeper understanding of the complexities surrounding data privacy pre-settlement, MEV, and frontrunning risks, offering insights into current practices and proposing thoughtful solutions to enhance user protection and market integrity.
What’s Next
We've now concluded our introductory series on the Oracle Standards: Architectures, Risk, and Security Paradigms. Up next, we'll embark on a series of more technical deep dives, dissecting the pillars outlined in our discussions. These upcoming sessions are designed to equip you with a robust mental model for in-depth understanding of Oracle security. Keep an eye out for our latest updates and dive deeper with us into the intricate world of Oracle security!
Oracle Risk and Security Standards: Network Architectures and Topologies (Pt. 2)
Oracle Network Architecture and Topologies provides a detailed examination of how Oracle Networks are structured, data’s complex journey from source to application, and the inherent security and risk considerations within these systems. Through a deep dive into architectures, the data supply chain, and network topology, readers will understand the critical components that ensure the functionality and reliability of Oracles in DeFi, providing context for the challenges and innovative solutions that define the landscape.
sBNB Oracle Exploit Post Mortem
Chaos Labs summarizes the snBNB oracle exploit affecting the Venus LST Isolated Pool. The post-mortem focuses on the event analysis and risk management efforts following the exploit.
Risk Less.
Know More.
Get priority access to the most powerful financial intelligence tool on the market.